Scalability is now on the forefront of the technical dialogue within the cryptocurrency scene. The Bitcoin blockchain is at the moment over 12 GB in measurement, requiring a interval of a number of days for a brand new bitcoind node to totally synchronize, the UTXO set that have to be saved in RAM is approaching 500 MB, and continued software program enhancements within the supply code are merely not sufficient to alleviate the pattern. With each passing 12 months, it turns into an increasing number of tough for an odd consumer to regionally run a totally useful Bitcoin node on their very own desktop, and at the same time as the value, service provider acceptance and recognition of Bitcoin has skyrocketed the variety of full nodes within the community has basically stayed the identical since 2011. The 1 MB block measurement restrict at the moment places a theoretical cap on this progress, however at a excessive value: the Bitcoin community can’t course of greater than 7 transactions per second. If the recognition of Bitcoin jumps up tenfold but once more, then the restrict will pressure the transaction charge as much as almost a greenback, making Bitcoin much less helpful than Paypal. If there may be one downside that an efficient implementation of cryptocurrency 2.0 wants to resolve, it’s this.
The rationale why we within the cryptocurrency spaceare having these issues, and are making so little headway towards arising with an answer, is that there one basic subject with all cryptocurrency designs that must be addressed. Out of all the numerous proof of labor, proof of stake and reputational consensus-based blockchain designs which were proposed, not a single one has managed to beat the identical core downside: that each single full node should course of each single transaction. Having nodes that may course of each transaction, even as much as a degree of 1000’s of transactions per second, is feasible; centralized programs like Paypal, Mastercard and banking servers do it simply effective. Nonetheless, the issue is that it takes a big amount of assets to arrange such a server, and so there isn’t a incentive for anybody besides just a few giant companies to do it. As soon as that occurs, then these few nodes are probably weak to revenue motive and regulatory strain, and will begin making theoretically unauthorized modifications to the state, like giving themselves free cash, and all different customers, that are depending on these centralized nodes for safety, would don’t have any approach of proving that the block is invalid since they don’t have the assets to course of the whole block.
In Ethereum, as of this level, now we have no basic enhancements over the precept that each full node should course of each transaction. There have been ingenious concepts proposed by numerous Bitcoin builders involving a number of merge-mined chains with a protocol for shifting funds from one chain to a different, and these will probably be a big a part of our cryptocurrency analysis effort, however at this level analysis into the best way to implement this optimally is just not but mature. Nonetheless, with the introduction of Block Protocol 2.0 (BP2), now we have a protocol that, whereas not getting previous the basic blockchain scalability flaw, does get us partway there: so long as not less than one sincere full node exists (and, for anti-spam causes, has not less than 0.01% mining energy or ether possession), “gentle shoppers” that solely obtain a small quantity of knowledge from the blockchain can retain the identical degree of safety as full nodes.
What Is A Mild Shopper?
The essential thought behind a lightweight shopper is that, thanks to an information construction current in Bitcoin (and, in a modified form, Ethereum) known as a Merkle tree, it’s potential to assemble a proof {that a} sure transaction is in a block, such that the proof is way smaller than the block itself. Proper now, a Bitcoin block is about 150 KB in measurement; a Merkle proof of a transaction is about half a kilobyte. If Bitcoin blocks turn into 2 GB in measurement, the proofs would possibly develop to an entire kilobyte. To assemble a proof, one merely must comply with the “department” of the tree all the way in which up from the transaction to the foundation, and supply the nodes on the aspect each step of the way in which. Utilizing this mechanism, gentle shoppers will be assured that transactions despatched to them (or from them) truly made it right into a block.
This makes it considerably tougher for malicious miners to trick gentle shoppers. If, in a hypothetical world the place working a full node was fully impractical for odd customers, a consumer needed to say that they despatched 10 BTC to a service provider with not sufficient assets to obtain the whole block, the service provider wouldn’t be helpless; they’d ask for a proof {that a} transaction sending 10 BTC to them is definitely within the block. If the attacker is a miner, they’ll probably be extra subtle and really put such a transaction right into a block, however have it spend funds (ie. UTXO) that don’t truly exist. Nonetheless, even right here there’s a protection: the sunshine shopper can ask for a second Merkle tree proof displaying that the funds that the ten BTC transaction is spending additionally exist, and so forth all the way down to some secure block depth. From the viewpoint of a miner utilizing a lightweight shopper, this morphs right into a challenge-response protocol: full nodes verifying transactions, upon detecting {that a} transaction spent an output that doesn’t exist, can publish a “problem” to the community, and different nodes (seemingly the miner of that block) would wish to publish a “response” consisting of a Merkle tree proof displaying that the outputs in query do truly exist in some earlier block. Nonetheless, there may be one weak spot on this protocol in Bitcoin: transaction charges. A malicious miner can publish a block giving themselves a 1000 BTC reward, and different miners working gentle shoppers would don’t have any approach of realizing that this block is invalid with out including up all the charges from all the transactions themselves; for all they know, another person may have been loopy sufficient to truly add 975 BTC price of charges.
BP2
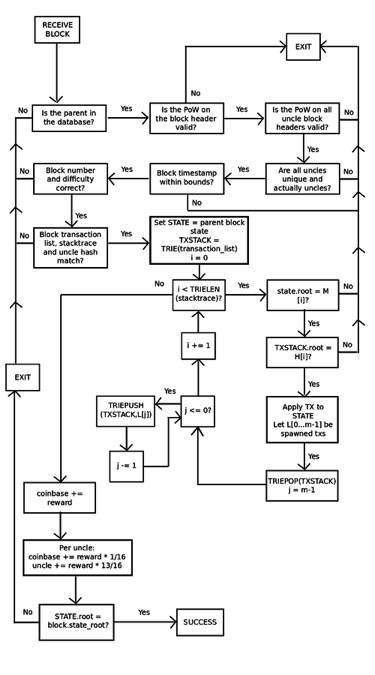
With the earlier Block Protocol 1.0, Ethereum was even worse; there was no approach for a lightweight shopper to even confirm that the state tree of a block was a sound consequence of the guardian state and the transaction listing. In truth, the one option to get any assurances in any respect was for a node to run by way of each transaction and sequentially apply them to the guardian state themselves. BP2, nevertheless, provides some stronger assurances. With BP2, each block now has three bushes: a state tree, a transaction tree, and a stack hint tree offering the intermediate root of the state tree and the transaction tree after every step. This permits for a challenge-response protocol that, in simplified kind, works as follows:
-
Miner M publishes block B. Maybe the miner is malicious, during which case the block updates the state incorrectly sooner or later.
-
Mild node L receives block B, and does fundamental proof of labor and structural validity checks on the header. If these checks go, then L begins off treating the block as legit, although unconfirmed.
-
Full node F receives block B, and begins doing a full verification course of, making use of every transaction to the guardian state, and ensuring that every intermediate state matches the intermediate state offered by the miner. Suppose that F finds an inconsistency at level okay. Then, F broadcasts a “problem” to the community consisting of the hash of B and the worth okay.
-
L receives the problem, and quickly flags B as untrustworthy.
-
If F’s declare is fake, and the block is legitimate at that time, then M can produce a proof of localized consistency by displaying a Merkle tree proof of level okay within the stack hint, level okay+1 within the stack hint, and the subset of Merkle tree nodes within the state and transaction tree that had been modified throughout the technique of updating from okay to okay+1. L can then confirm the proof by taking M’s phrase on the validity of the block as much as level okay, manually working the replace from okay to okay+1 (this consists of processing a single transaction), and ensuring the foundation hashes match what M offered on the finish. L would, after all, additionally examine that the Merkle tree proof for the values at state okay and okay+1 is legitimate.
-
If F’s declare is true, then M wouldn’t be capable of give you a response, and after some time frame L would discard B outright.
Notice that at the moment the mannequin is for transaction charges to be burned, not distributed to miners, so the weak spot in Bitcoin’s gentle shopper protocol doesn’t apply. Nonetheless, even when we determined to alter this, the protocol can simply be tailored to deal with it; the stack hint would merely additionally hold a working counter of transaction charges alongside the state and transaction listing. As an anti-spam measure, to ensure that F’s problem to be legitimate, F must have both mined one of many final 10000 blocks or have held 0.01% of the entire provide of ether for not less than some time frame. If a full node sends a false problem, that means {that a} miner efficiently responds to it, gentle nodes can blacklist the node’s public key.
Altogether, what this implies is that, not like Bitcoin, Ethereum will seemingly nonetheless be totally safe, together with towards fraudulent issuance assaults, even when solely a small variety of full nodes exist; so long as not less than one full node is sincere, verifying blocks and publishing challenges the place acceptable, gentle shoppers can depend on it to level out which blocks are flawed. Notice that there’s one weak spot on this protocol: you now must know all transactions forward of time earlier than processing a block, and including new transactions requires substantial effort to recalculate intermediate stack hint values, so the method of manufacturing a block will probably be extra inefficient. Nonetheless, it’s seemingly potential to patch the protocol to get round this, and whether it is potential then BP2.1 can have such a repair.
Blockchain-based Mining
We’ve got not finalized the small print of this, however Ethereum will seemingly use one thing much like the next for its mining algorithm:
-
Let H[i] = sha3(sha3(block header with out nonce) ++ nonce ++ i) for i in [0 …16]
-
Let N be the variety of transactions within the block.
-
Let T[i] be the (H[i] mod N)th transaction within the block.
-
Let S be the guardian block state.
-
Apply T[0] … T[15] to S, and let the ensuing state be S’.
-
Let x = sha3(S’.root)
-
The block is legitimate if x * problem <= 2^256
This has the next properties:
-
That is extraordinarily memory-hard, much more so than Dagger, since mining successfully requires entry to the whole blockchain. Nonetheless it’s parallelizable with shared disk house, so it’ll seemingly be GPU-dominated, not CPU-dominated as Dagger initially hoped to be.
-
It’s memory-easy to confirm, since a proof of validity consists of solely the comparatively small subset of Patricia nodes which are used whereas processing T[0] … T[15]
-
All miners basically need to be full nodes; asking the community for block information for each nonce is prohibitively gradual. Thus there will probably be a bigger variety of full nodes in Ethereum than in Bitcoin.
-
On account of (3), one of many main motivations to make use of centralized mining swimming pools, the truth that they permit miners to function with out downloading the whole blockchain, is nullified. The opposite foremost cause to make use of mining swimming pools, the truth that they even out the payout price, will be assomplished simply as simply with the decentralized p2pool (which we are going to seemingly find yourself supporting with growth assets)
-
ASICs for this mining algorithm are concurrently ASICs for transaction processing, so Ethereum ASICs will assist remedy the scalability downside.
From right here, there may be solely actually one optimization that may be made: determining some option to get previous the impediment that each full node should course of each transaction. It is a laborious downside; a very scalable and efficient resolution will take some time to develop. Nonetheless, this can be a robust begin, and will even find yourself as one of many key elements to a closing resolution.